Building Information Modeling (BIM)
BIM technology is changing the way architects, engineers, and construction professionals collaborate. It enables the creation of a detailed digital representation of a building, complete with all its components and systems. This digital twin helps streamline the construction process, reduce errors, and enhance project management, resulting in significant cost and time savings.
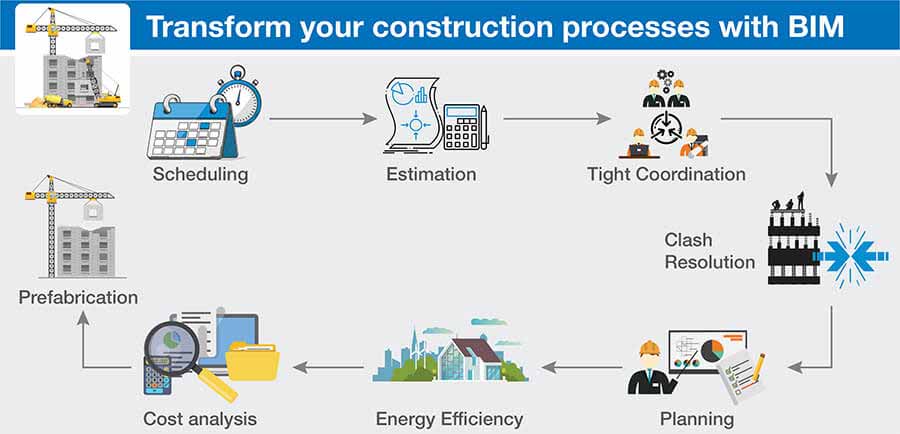
Building Information Modeling (BIM): Revolutionizing Construction from Design to MaintenanceBuilding Information Modeling (BIM) is another game-changing technology that has transformed the construction industry. BIM goes beyond traditional 2D blueprints and CAD drawings, offering a comprehensive digital representation of a building and all its components. It is a dynamic and collaborative tool that has far-reaching implications for the construction process, from initial design to ongoing maintenance and facility management.
The Essence of BIM:
At its heart, BIM is a digital model of a building or infrastructure project. Unlike static drawings, BIM incorporates a wealth of data and information that can be utilized throughout the project's lifecycle. This includes geometric data, spatial relationships, material specifications, and even information about the building's energy performance.
Key Benefits of BIM:
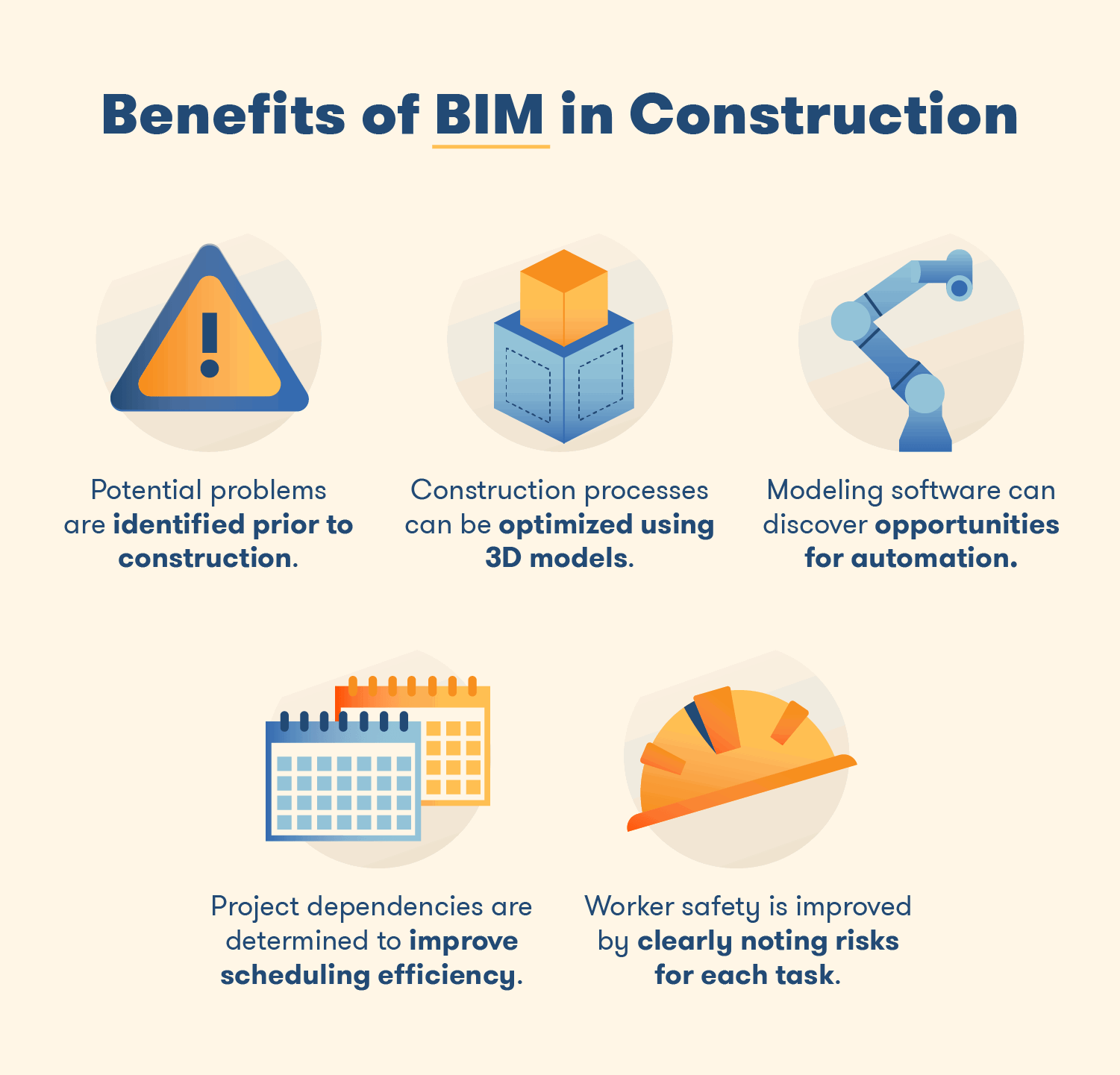
- Enhanced Collaboration: BIM encourages collaboration and information sharing among all stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, and owners. This collaborative approach helps in avoiding miscommunication and reduces errors during the design and construction phases.
- Improved Design Quality: BIM enables designers to visualize the project in 3D, making it easier to identify design flaws or clashes early in the process. This leads to higher-quality designs and fewer costly changes during construction.
- Cost and Time Savings: BIM's ability to simulate the construction process and provide accurate quantity take-offs helps in better cost estimation and project scheduling. This results in reduced project overruns and delays.
- Facility Management: BIM data extends beyond construction; it can be used for facility management and maintenance. Owners can access information about every aspect of the building, from the type of lightbulbs used to maintenance schedules for HVAC systems.
- Sustainability: BIM can support sustainable design by providing insights into energy performance, material efficiency, and other environmental factors. This helps in designing and constructing greener, more energy-efficient buildings.


